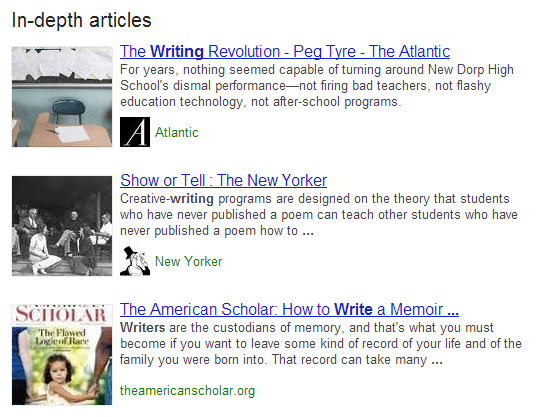
Google Search now highlights quality, in-depth articles related to search queries. When searching for broad terms such as “management” or “writing”, the first results page will include an “In-depth articles” section at the bottom.
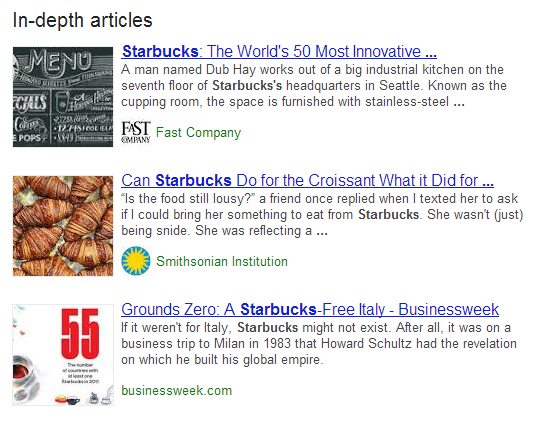
The in-depth articles section lists three articles at a time, and it also appears when searching for certain brand names like “Lego” or “Starbucks”. It only appears in English-language search for now, but Google will continue rolling the feature out over the next few days.
Google developed this new feature based on the results of their Daily Information Needs study. This study revealed that about 10% of people require more than quick answers when searching for a broad topic on Google. Pandu Nayak, a member of Google’s Technical Staff, announced this new feature on Google Search’s official blog. “I’m happy to see people continue to invest in thoughtful in-depth content that will remain relevant for months or even years after publication,” he said. “This is exactly what you’ll find in the new feature. In addition to well-known publishers, you’ll also find some great articles from lesser-known publications and blogs.”
How to Appear in “In-depth Articles” Results
Writing compelling, high-quality content is the best way to improve a website’s search rankings, but getting a website’s content to appear in Google’s in-depth articles list requires a different kind of optimization. Google provided the following tips for anyone who wants to optimize content for the in-depth articles feature:
- schema.org Article markups: Using schema.org Article markups will help Google understand a page’s content better through richer metadata. Google lists the following schema.org markups as the most important when optimizing a page for in-depth search results:
- headline
- alternativeHeadline
- image (the image must also be crawlable/indexable)
- description
- datePublished
- articleBody
- Authorship: Authorship markups help Google identify industry authors and experts. This requires authors to include direct links to their Google+ profiles in their content, or to use verified email addresses to link their content and their profiles.
- Pagination and Canonicalization for Multi-Part Content: In-depth content that goes beyond a single page need proper pagination markups. These help Google identify the article’s length and the extent of its coverage. Canonicalization markups should point to each individual page, or to a view-all page instead of the first page of a multi-part series.
- Source Logos: Including a company logo in content will help users recognize and remember its source. Specify a logo by using organization markups, or by linking the company’s Google+ page to the website.
- First Click Free: Google can’t crawl or index content that requires visitors to register, subscribe, or login. The First Click Free feature allows Googlebot and first-time visitors to view the full content without registering. Webmasters can require users to register or sign-in when they click on another link in the page.
The in-depth articles feature does not appear for all broad topic searches yet, but optimizing your website’s content as soon as possible will give your brand a good head start.
